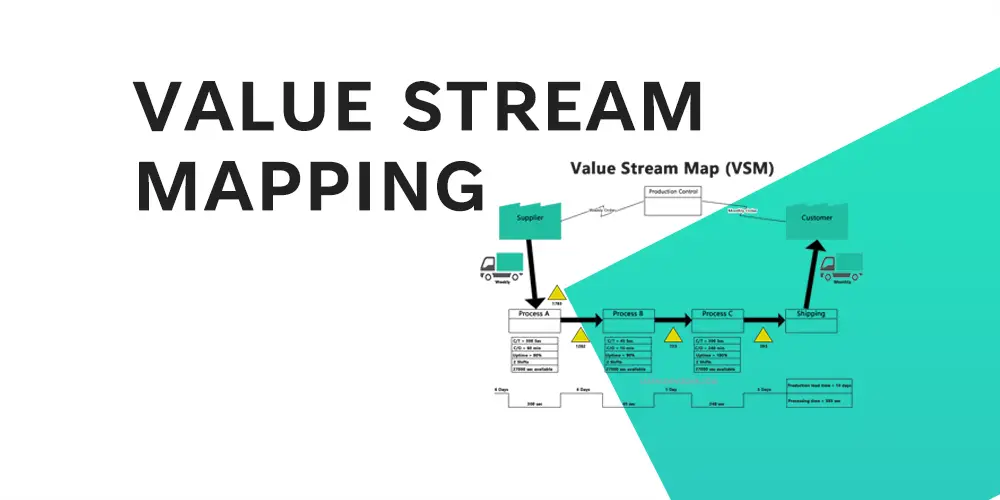
What is Value Stream Mapping?
Value Stream Mapping (VSM) is a lean methodology used to analyse and design the flow of materials and information in a manufacturing or service process. The goal is to identify and eliminate waste, streamline processes, increase efficiency, and improve customer satisfaction. It illustrates the current and future state of a process, assisting in the identification of areas for improvement and facilitating communication and collaboration among team members.
VSM’s goal is to create a lean and efficient process that reduces waste while increasing customer satisfaction. VSM assists teams in identifying and addressing the root causes of inefficiencies, as well as improving the overall performance of the process, by visualizing the entire process.

The History of Value Stream Mapping
Value Stream Mapping is based on the Toyota Production System and lean manufacturing principles. Toyota implemented a series of manufacturing process improvements in the mid-twentieth century, resulting in increased efficiency, reduced waste, and improved customer satisfaction. The Toyota Production System was based on the principles of continuous improvement and waste elimination (also known as “muda” in Japanese).
A group of American engineers and consultants, including James P. Womack and Daniel T. Jones, studied the Toyota Production System and developed the concept of lean manufacturing in the late 1980s and early 1990s. The term “value stream” was coined to describe the flow of materials and information from raw materials to the customer. They also created the Value Stream Mapping technique as a tool for analyzing and designing the flow of materials and information in a manufacturing process.
Value Stream Mapping has been widely adopted in the manufacturing and service industries since its inception, and it has been adapted to other fields such as healthcare, construction, and software development. VSM has grown in popularity among businesses looking to reduce waste, streamline processes, and boost efficiency and customer satisfaction.
The Benefits of Value Stream Mapping
Value Stream Mapping provides a number of benefits for organizations looking to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of their processes:
- Better process flow: VSM assists organizations in visualizing and analyzing the flow of materials and information in a process, allowing them to identify waste and inefficiency and implement improvements to streamline the process.
- Reduce waste: Organizations can improve the efficiency of their processes and reduce costs by eliminating waste such as overproduction, waiting, defects, overprocessing, and unused talent.
- Increased customer satisfaction: By improving process flow and reducing waste, organizations can increase the speed and reliability of their deliveries, resulting in higher levels of customer satisfaction.
- Improved communication and collaboration: VSM provides a common visual language and framework for process improvement, which can help team members communicate and collaborate more effectively.
- Improved process understanding: VSM provides a comprehensive view of the process, including all steps involved, the flow of materials and information, and the time, resources, and inventory required at each step. This knowledge can be used to identify areas for improvement and to implement changes that will increase efficiency and lower costs.
Overall, Value Stream Mapping is an effective tool for organizations seeking to increase the efficiency and effectiveness of their processes. Organizations can significantly improve process performance and customer satisfaction by visualizing the flow of materials and information and eliminating waste.
The Challenges of Value Stream Mapping
While Value Stream Mapping has many advantages, it also has some drawbacks when it comes to implementation:
- Time and resource limitations: VSM can be a time-consuming process that necessitates a substantial investment of time and resources. Organizations with limited resources and competing priorities may find this difficult.
- Change resistance: Implementing improvements based on VSM insights may necessitate significant changes to existing processes, workflows, and technology. Employees who are accustomed to the current way of doing things may be resistant.
- Difficulty in implementation: VSM provides a visual representation of the process, but turning this into tangible improvements can be challenging. Organizations must have the necessary skills and resources in place to implement the VSM-identified improvements.
- Maintaining momentum: Improving is a continuous process, and it can be difficult to maintain momentum and focus on continuous improvement over time.
- Lack of buy-in: VSM requires buy-in at all organizational levels, including management, employees, and stakeholders. Without this buy-in, the implementation of VSM and the improvements that result may be limited.
- Limited scope: VSM provides a comprehensive view of the process, but it may not take into account other factors that impact the process, such as the broader organizational culture and external factors such as regulations and market conditions.
Despite these obstacles, Value Stream Mapping remains an important tool for organizations seeking to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of their processes. Organizations can realize the many benefits of VSM and achieve significant improvements in process performance and customer satisfaction by carefully managing these challenges.
How Value Stream Mapping Identifies and Reduces Waste
By providing a comprehensive visual representation of the flow of materials and information in a process, Value Stream Mapping (VSM) assists organizations in identifying and reducing waste. VSM analyses this flow to assist organizations in identifying waste and inefficiency, such as:
- Overproduction: Producing more than what the customer requires, resulting in increased inventory levels and storage costs.
- Waiting: Time lost due to idle workers, equipment, or materials waiting for the next step in the process.
- Defects: Materials, products, or services that were rejected due to errors or poor quality.
- Overprocessing: Steps in the process that are unnecessary or redundant and add no value to the customer.
- Unused talent: Underutilized skills and knowledge of employees.
Organizations can implement improvements to streamline the process and eliminate waste by identifying these waste areas. For example, better forecasting and inventory management can help reduce overproduction, while cross-training and improved equipment utilization can help reduce waiting. Defect reduction can be accomplished through improved quality control processes, while over processing reduction can be accomplished through process simplification and standardization. Organizations can improve the efficiency of their processes, lower costs, and increase customer satisfaction by reducing waste.
The Value Stream Mapping Symbols
The various elements of a process are represented by a set of icons in Value Stream Mapping (VSM). VSM icons differ depending on the methodology and tool used, but some common icons include
- Material flow icons: Represent the flow of materials through the process, such as raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods.
- Information flow icons: Represent the flow of information through the process, such as customer orders, invoices, and production schedules.
- Process icons: Represent the various steps in the process, such as manufacturing, assembly, inspection, and packaging.
- Inventory icons: Show how much inventory is held at each stage of the process, such as raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods.
- Supplier icons: Represent the suppliers of materials, components, or services to the process.
- Customer icons: Represent the customers or end-users of the products or services produced by the process.
- Wait icons: Show the amount of time lost due to idle workers, equipment, or materials while waiting for the next step in the process.
- Inspection icons: Represent the quality assurance inspection of materials, products, or services.
- Flow line icons: Show how materials and information flow through the process.

VSM provides a visual representation of the process through the use of these icons, allowing organizations to see the flow of materials and information, identify areas of waste and inefficiency, and implement improvements to streamline the process. Icons are used in VSM to help simplify the process and make it easier to understand and communicate.
How to Create and Value Steam Map
Here are the steps to create a Value Stream Map:
- Define the scope: Determine the process or product family to map, and define the map’s boundaries in terms of inputs, outputs, and customers.
- Collect information: Gather process information such as process times, cycle times, inventory levels, and production schedules. You can also collect information about customer needs, such as lead times and delivery dates.
- Draw the current state map: Draw a visual representation of the process using a standard set of icons to represent the various elements, such as materials flow, information flow, processes, inventory, suppliers, and customers. Each step in the process should be labelled, and relevant data such as cycle times, inventory levels, and lead times should be included.
- Investigate the current state map: Overproduction, waiting, defects, overprocessing, and unused talent are examples of waste and inefficiency.
- Create a future state map: Using the insights gained from the current state map analysis, create a future state map that eliminates waste and streamlines the process. This could include streamlining the process, shortening cycle times, and improving inventory management.
- Identify the improvements: Determine the specific changes that will be made to the process in order to achieve the future state map, and priorities these changes based on their impact and feasibility.
- Implement the improvements: Implement the improvements identified in the previous step, such as process simplification, cross-training, and improved inventory management.
- Monitor and review: Continuously monitor the process to ensure that the improvements are having the desired effect, and make further improvements as needed.
Organizations can create a Value Stream Map by following these steps, which provides a visual representation of the process, assists in identifying areas of waste and inefficiency, and supports the implementation of improvements to streamline the process and increase efficiency. VSM enables organizations to focus on continuous improvement, cost reduction, and customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Value Stream Mapping is a powerful tool for organisations looking to improve their processes and increase efficiency. VSM allows organizations to identify areas of waste and inefficiency and implement improvements to streamline the process by creating a visual representation of the process. VSM is used to support a continuous improvement approach, lowering costs and increasing customer satisfaction. Organizations can create a VSM that provides a clear picture of the process and helps drive improvements to increase efficiency and effectiveness by following a step-by-step process.