I-MR Chart (Individual & Moving Range Control Chart)
Results
Feedback
Data Validation Error
Uploaded data contains invalid values. Please upload a valid CSV or XLSX with numerical values.
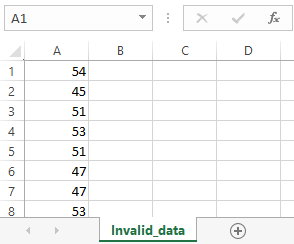
Example of correct format:
The Control Chart Analysis Tool offers a robust method for monitoring and analyzing the stability and performance of processes over time. Rooted in the principles of statistical process control, this tool provides real-time insights, highlighting variations and potential areas for improvement. By visualizing data trends, users can easily distinguish between common and special cause variations, enabling timely and informed decision-making. The tool also seamlessly integrates features like Upper and Lower Control Limits (UCL and LCL) and provides immediate feedback, assisting professionals in ensuring process consistency. With an intuitive interface, built-in export capabilities, and watermarking features, this tool is an indispensable asset for quality assurance professionals, process engineers, and anyone keen on driving process excellence.
Press “Demo” for an Example
Uploading Data
- Click on the ‘Load Data’ button.
- Select your CSV file with process data. Ensure your data is formatted correctly, with each value on a new line.
Viewing the Control Chart
Once data is uploaded, the tool will automatically generate a control chart showcasing the process variation, mean, UCL, and LCL.
Understanding the Feedback
Beneath the control chart, you’ll find the ‘Feedback’ section, providing insights and interpretations based on your data.
Exporting the Analysis
- To PDF: Click on the ‘Export Control Chart to PDF’ button. This will generate a comprehensive report, inclusive of the chart, key metrics, and feedback.
- To Image: Click on the ‘Export Chart to Image’ button.
Interactivity and Customization
Hover over specific data points on the control chart to get more detailed information. You can also adjust the chart’s appearance and scale using the provided settings.
Resetting the Tool
To analyze a new set of data or to start afresh, click on the ‘Reset’ button. This will clear all previous data and feedback.
Tips for Optimal Use
- Ensure your data is free of any anomalies before uploading.
- Regularly use the tool for consistent monitoring of process variations.
- Leverage the feedback section to make informed decisions about your process.
Control Charts: Overview and Uses
What are Control Charts?
Control charts, also known as process-behavior charts or Shewhart charts (after Walter A. Shewhart, who developed the concept), are a type of statistical process control (SPC) tool. They are used to determine if a process is stable and predictable, based on how data points vary over time.
A typical control chart consists of:
- A central line representing the mean (or another measure of central tendency) of the data.
- Upper and Lower Control Limits (UCL and LCL), which are set distances from the central line. They help in identifying variations that are due to specific events or causes rather than random factors.
- Data points plotted over time.
Uses and Benefits of Control Charts:
- Process Monitoring and Control: Control charts allow businesses to monitor processes in real-time and detect deviations from the norm. This helps in taking corrective actions promptly.
- Identifying Variability: Control charts distinguish between common-cause variation (natural and inherent to the process) and special-cause variation (due to specific factors or events). This is crucial for understanding the root causes of problems.
- Improving Process Consistency: By identifying and eliminating sources of special-cause variation, control charts aid in making processes more consistent and predictable.
- Optimizing Process Performance: Control charts can help set realistic performance targets based on process capabilities and identify areas for improvement.
- Supporting Decision Making: They provide objective data, making it easier for managers and teams to make informed decisions rather than relying on gut feelings or unstructured observations.
- Quality Assurance: In manufacturing and other sectors, control charts help ensure that products or services meet quality standards consistently.
- Reducing Costs: By identifying inefficiencies and deviations early, businesses can prevent defects, rework, and waste, leading to cost savings.
- Benchmarking: Control charts can be used to compare the performance of different processes or shifts, or benchmark against industry standards.
- Compliance and Documentation: In regulated industries, control charts can serve as documentation to prove that processes are under control and meet required standards.
In Conclusion:
Control charts are a cornerstone of quality improvement methodologies like Six Sigma and Lean. They provide a visual representation of process performance, allowing businesses to maintain consistent quality, improve efficiency, and react quickly to deviations. Whether in manufacturing, healthcare, finance, or any other sector, control charts are an indispensable tool for continuous improvement and operational excellence.




